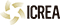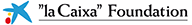A crucial mechanism for multicellularity is highly conserved in closest unicellular relative of animals
A crucial mechanism for multicellularity is highly conserved in closest unicellular relative of animals
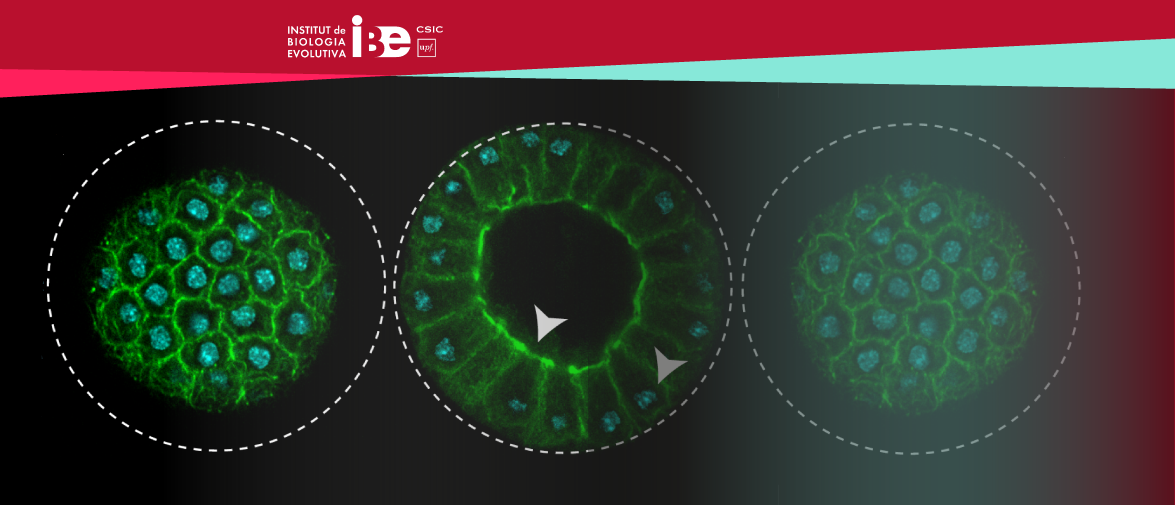
IBE Researchers led by Iñaki Ruiz-Trillo have identified that a unicellular relative of animals undergoes a transient stage resembling an epithelium tissue.
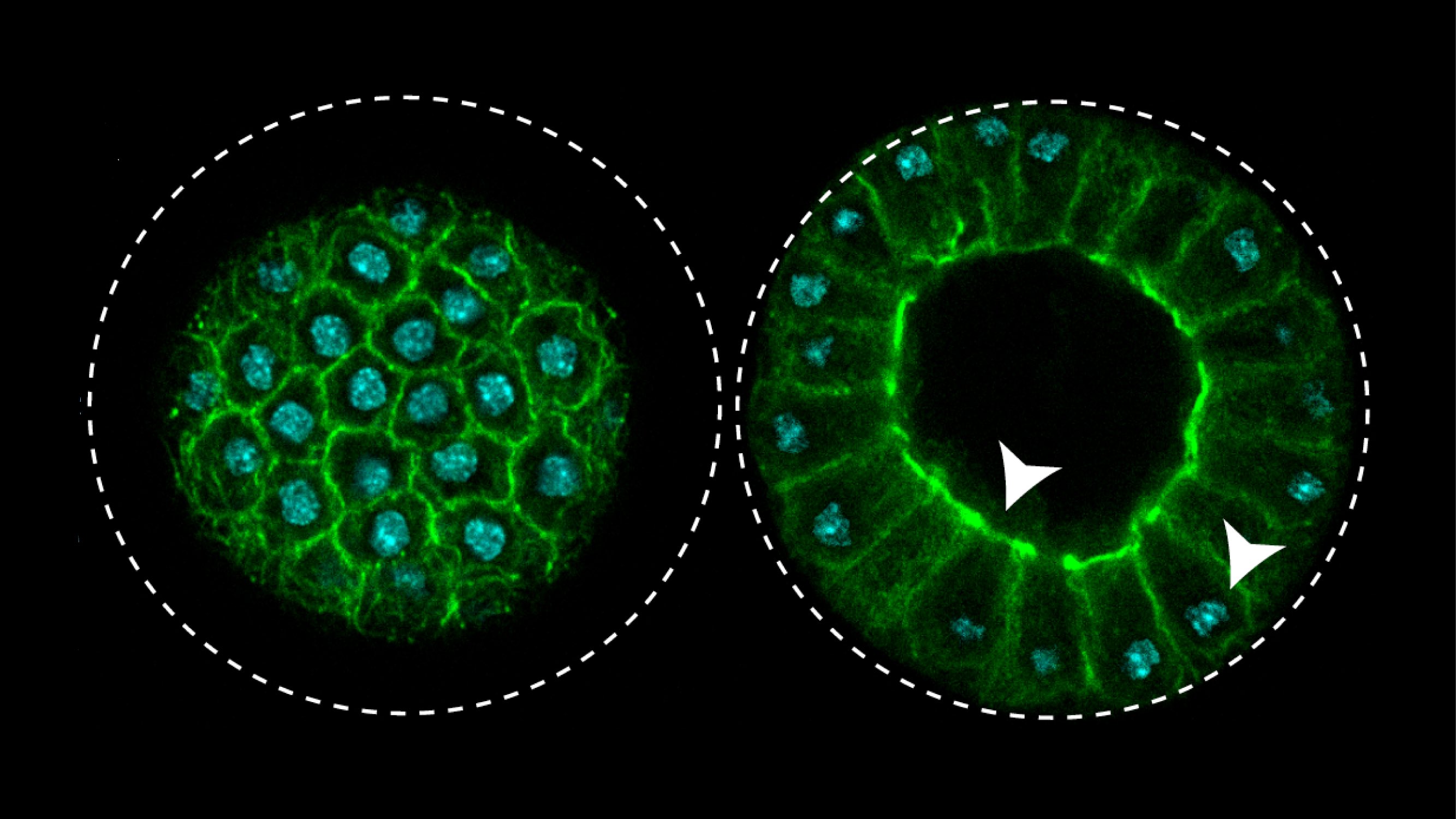
The process, observed during coordinated cellularization of the protist Sphaeroforma arctica, resembles cellularization of coenocyte in animals, a specialized form of cytokinesis that results in the formation of a polarized epithelium during early embryonic development. Researchers have shown that the polarized layer of cells in Sphaeroforma arctica relies, as in animals, on an actomyosin network to hold the transient structure and that the temporary stage goes in hand with the activation of genes involved in cell adhesion.
Reference article: Dudin O, Ondracka A, Grau-Bové X, Haraldsen AAB, Toyoda A, Suga H, Bråte J, Ruiz-Trillo I. A unicellular relative of animals generates a layer of polarized cells by actomyosin-dependent cellularization. eLife 2019;8:e49801.